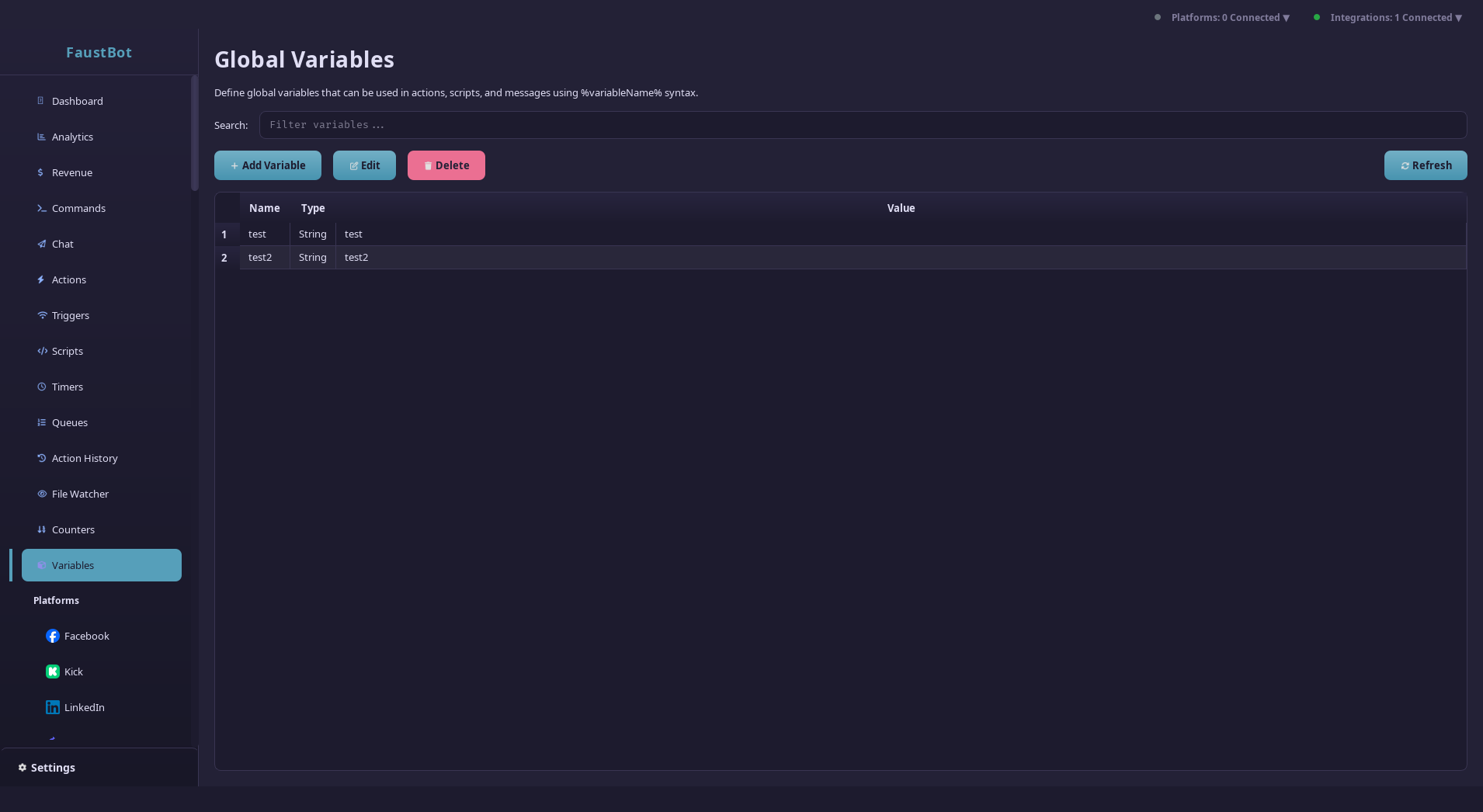
Variables
Variables let you store, retrieve, and manipulate data in your automations. Use them to create dynamic responses, track statistics, and build complex workflows.
Overview
FaustBot's variable system supports multiple data types, scopes, and persistence options. Variables can come from event context, be set by actions, or be registered by plugins.
Variable Sources
- Event Context - Automatically set when triggers fire
- User-Defined - Created via Set Variable effect or scripts
- Plugin Variables - Provided by platform and integration plugins
- System Variables - Built-in values like date, time, counters
Variable Types
FaustBot supports several data types with automatic type inference and coercion.
String
Text values of any length
"Hello, world!"Integer
Whole numbers (64-bit)
42, -100, 9999Double
Floating-point numbers
3.14, -0.5, 100.0Boolean
True or false values
true, falseDateTime
Date and time values
2024-01-15T14:30:00List
Ordered arrays of values
["a", "b", "c"]Object
Key-value maps
{"name": "value"}Null
Explicit empty value
nullVariable Scopes
Variables can be stored at different scopes depending on how long they should persist and who should have access.
Global
Shared across all users and sessions. Persists between restarts.
SetGlobalVar("totalFollowers", count) GetGlobalVar("streamTitle")User
Unique per user. Great for user-specific stats and preferences.
SetUserVar(userId, "points", 100) GetUserVar(userId, "watchTime")Session
Persists for the current stream session only.
SetSessionVar("deathCount", 0) GetSessionVar("songQueue")Temporary
Only available during the current action execution.
%tempResult% Automatically cleared after action
Substitution Syntax
Use the %variableName% syntax to substitute variable values in effect parameters.
Basic Substitution
Hello, %user%! → Hello, StreamerFan99!
You have %points% points. → You have 1500 points.
Stream title: %streamTitle% → Stream title: Gaming with viewers!Nested Properties
Access nested object properties with dot notation:
%user.displayName% → "CoolStreamer"
%user.badges.vip% → true
%event.amount% → 5.00Array Access
Access array elements by index:
%queue[0]% → First item in queue
%winners[2]% → Third winner
%args[1]% → Second command argumentDefault Values
Provide fallback values for missing variables:
%nickname|%user%% → Use nickname, fall back to user
%points|0% → Use points, default to 0
%greeting|Hello!% → Use greeting, default to "Hello!"Inline Expressions
Use $expression$ syntax for math operations and function calls.
Math Operations
$5 + 3$ → 8
$points * 2$ → Double the points
$total / count$ → Average
$score % 10$ → Remainder (modulo)
$(base + bonus) * 1.5$ → Grouped operationsComparison
$points > 100$ → true/false
$level >= 5$ → true/false
$name == "admin"$ → true/false
$status != "offline"$ → true/falseBuilt-in Functions
String Functions
$upper(text)$ Convert to uppercase$lower(text)$ Convert to lowercase$length(text)$ Get string length$trim(text)$ Remove whitespace$substring(text, start, len)$ Extract substring$replace(text, find, replace)$ Replace occurrencesNumber Functions
$random(min, max)$ Random integer in range$round(num)$ Round to nearest integer$floor(num)$ Round down$ceil(num)$ Round up$abs(num)$ Absolute value$min(a, b)$ Smaller of two values$max(a, b)$ Larger of two valuesDate/Time Functions
$now()$ Current date/time$today()$ Current date (no time)$formatDate(date, format)$ Format date string$timestamp()$ Unix timestamp (seconds)Type Coercion
FaustBot automatically converts between types when needed. Understanding these rules helps avoid unexpected behavior.
| From | To | Result |
|---|---|---|
| String "42" | Integer | 42 (parsed) |
| Integer 42 | String | "42" |
| Integer 42 | Double | 42.0 (lossless) |
| Double 3.7 | Integer | 3 (truncated) |
| Integer 0 | Boolean | false |
| Integer 1+ | Boolean | true |
| String "true" | Boolean | true |
| DateTime | Integer | Unix timestamp |
Coercion Quality
- Lossless - No data lost (e.g., int → double)
- Lossy - Some precision lost (e.g., double → int)
- Invalid - Conversion fails (e.g., "abc" → int)
Scripting Access
Access variables from C# and C++ scripts using the CPH API.
C# Examples
// Global variables
string title = CPH.GetGlobalVar<string>("streamTitle");
int followers = CPH.GetGlobalVar<int>("totalFollowers", 0);
// User variables
int points = CPH.GetUserVar<int>(userId, "points", 0);
DateTime lastSeen = CPH.GetUserVar<DateTime>(userId, "lastSeen");// Global variables
CPH.SetGlobalVar("streamTitle", "New Title!");
CPH.SetGlobalVar("isLive", true);
// User variables
CPH.SetUserVar(userId, "points", newPoints);
CPH.SetUserVar(userId, "lastCommand", DateTime.Now);
// Persistent (survives restart)
CPH.SetGlobalVar("lifetimeSubs", count, true);// Remove global variable
CPH.UnsetGlobalVar("tempData");
// Remove user variable
CPH.UnsetUserVar(userId, "oldPoints");Accessing Event Data
public bool Execute() {
// Event data is passed in args
string user = args["user"].ToString();
string message = args["message"].ToString();
bool isMod = args.ContainsKey("isModerator")
&& (bool)args["isModerator"];
// Platform-specific data
if (args.ContainsKey("bits")) {
int bits = (int)args["bits"];
}
return true;
}