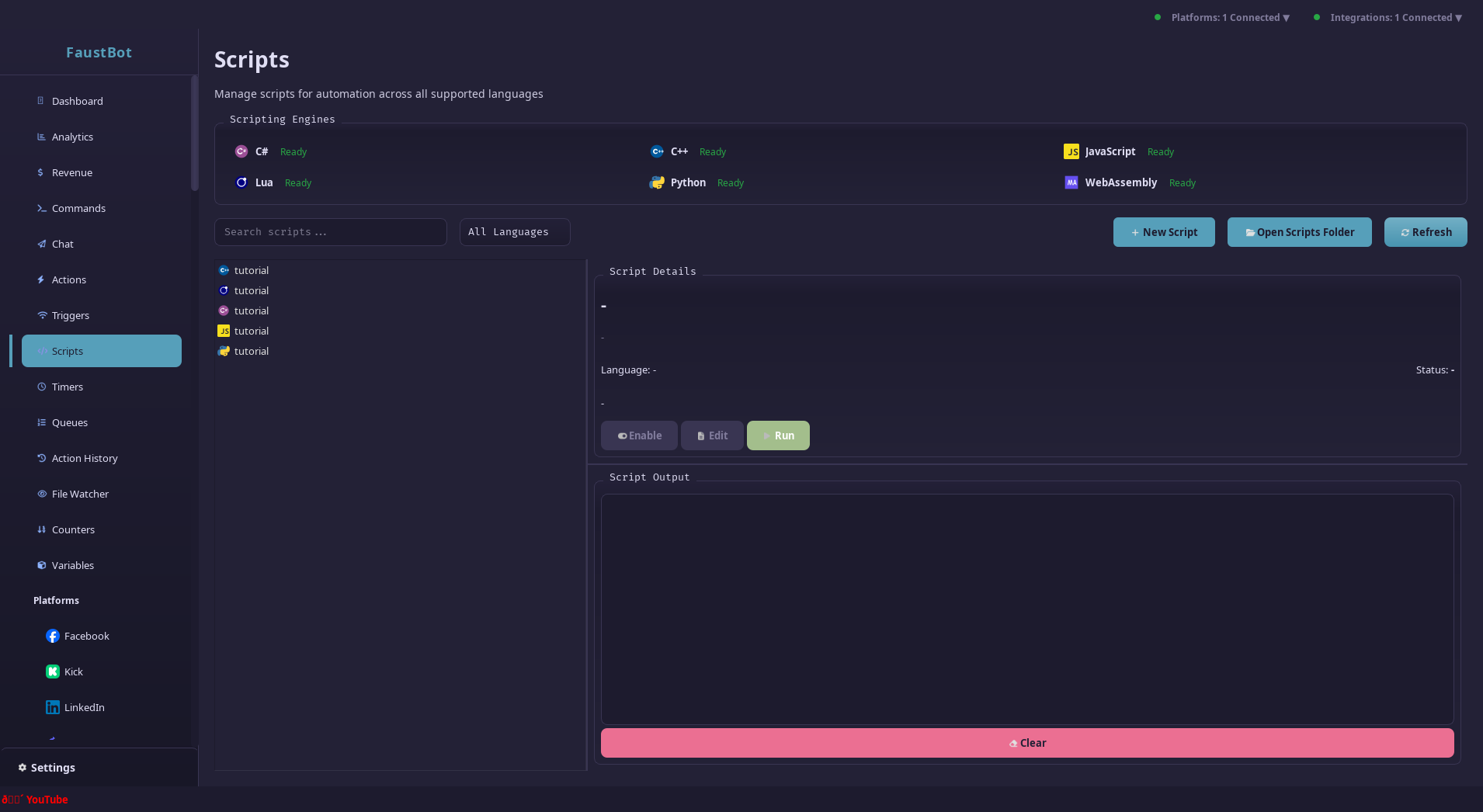
Scripting
Extend FaustBot's capabilities with custom scripts. Write complex logic, integrate external APIs, and create unique automations using your preferred language.
Overview
FaustBot's scripting system lets you write custom code that executes within your actions. Scripts have full access to the CPH API, allowing you to interact with platforms, manage variables, control OBS, and much more.
When to Use Scripts
- Complex conditional logic beyond if/else
- Custom API integrations
- Data processing and transformation
- Advanced math and string manipulation
- Integration with external services
Supported Languages
FaustBot supports multiple scripting languages through its plugin system.
Python (Recommended)
Popular language with extensive libraries and easy syntax.
- Easy to learn
- Rich ecosystem
- Data processing
Lua (Recommended)
Lightweight scripting, perfect for simple to moderate tasks.
- Simple syntax
- Fast startup
- Game dev friendly
JavaScript
Familiar syntax for web developers.
- Familiar syntax
- Async support
- JSON handling
C#
Full .NET support with strong typing and excellent tooling.
- Strong typing
- Full API access
- IDE support
C++ / WASM
Native performance for computationally intensive tasks.
- WebAssembly support
- Maximum performance
- Low-level control
Your First Script
Let's create a simple script that sends a message to chat. The structure varies slightly between languages, but the API calls are the same.
Create a Script Effect
In your action, add a Run Script effect and select your language.
Write the Code
Every script needs an Execute() function that returns a boolean.
Return true to continue the action, or false to stop.
def Execute():
# Your code here
CPH.SendMessage("Hello from script!")
return TrueTest the Script
Save your action and trigger it. Check the logs for any errors.
Script Tips
- Always handle exceptions to prevent action failures
- Use
CPH.LogInfo()to debug your scripts - Keep scripts focused on a single task
- Test with different input scenarios
The CPH API
The CPH object provides access to all of FaustBot's functionality.
It's automatically available in all scripts.
Working with Variables
Get and set global and user-scoped variables:
# Global variables
title = CPH.GetGlobalVar("streamTitle")
followers = CPH.GetGlobalVar("totalFollowers", 0)
# User variables
points = CPH.GetUserVar(user_id, "points", 0)
last_seen = CPH.GetUserVar(user_id, "lastSeen")
# Set variables
CPH.SetGlobalVar("streamTitle", "New Title!")
CPH.SetUserVar(user_id, "points", new_points)
# Persistent (survives restart)
CPH.SetGlobalVar("lifetimeSubs", count, True)API Quick Reference
Logging
CPH.LogVerbose(message) Detailed debug loggingCPH.LogDebug(message) Debug informationCPH.LogInfo(message) General informationCPH.LogWarn(message) WarningsCPH.LogError(message) ErrorsChat & Messaging
CPH.SendMessage(message, bot?) Send chat messageCPH.SendWhisper(user, message) Send whisper/DMCPH.TwitchAnnounce(message, color?) Send announcementActions
CPH.RunAction(name, runImmediately?) Run action by nameCPH.RunActionById(id, runImmediately?) Run action by IDCPH.DisableAction(name) Disable an actionCPH.EnableAction(name) Enable an actionTwitch
CPH.TwitchBanUser(user, reason?) Ban a userCPH.TwitchTimeoutUser(user, duration, reason?) Timeout a userCPH.TwitchSetTitle(title) Set stream titleCPH.TwitchSetGame(game) Set stream categoryOBS
CPH.ObsSetScene(scene) Switch sceneCPH.ObsShowSource(scene, source) Show sourceCPH.ObsHideSource(scene, source) Hide sourceCPH.ObsSetSourceFilterState(source, filter, state) Toggle filterSee the full API reference for complete documentation.
Accessing Event Data
When a trigger fires, event data is passed to your script through the args dictionary/object.
def Execute():
# Basic event info
user = args["user"]
display_name = args["displayName"]
message = args["message"]
platform = args["platform"]
# User roles (bool)
is_mod = args.get("isModerator", False)
is_sub = args.get("isSubscriber", False)
# Platform-specific data
if "bits" in args:
bits = int(args["bits"])
CPH.SendMessage(f"Thanks for the {bits} bits!")
return TrueSetting Output Variables
Scripts can set variables that are available to subsequent effects in the same action.
def Execute():
# Calculate something
result = calculate_something()
# Make it available to other effects
CPH.SetArgument("myResult", result)
CPH.SetArgument("processed", True)
return True
# Later effects can use %myResult% and %processed%Script Permissions
Scripts can be restricted by permission flags for security. By default, scripts run with standard permissions.
| Permission | Allows |
|---|---|
FileRead | Read files from disk |
FileWrite | Write files to disk |
Network | Make HTTP requests |
Process | Execute system processes |
Database | Direct database access |
Twitch | Twitch API calls |
YouTube | YouTube API calls |
OBS | OBS WebSocket commands |
Permission Presets
- Safe - Variables, Actions, Commands (no external access)
- Standard - Safe + FileRead, Audio, TTS, Platform APIs
- Network - Standard + HTTP requests, Discord
- Full - All permissions (use with caution)
Debugging
Use logging and the script console to debug issues.
Logging
def Execute():
CPH.LogInfo("Script started")
try:
user = args["user"]
CPH.LogDebug(f"Processing user: {user}")
# Your logic here
result = do_something()
CPH.LogInfo(f"Result: {result}")
return True
except Exception as e:
CPH.LogError(f"Script failed: {e}")
return FalseScript Console
The Script Console shows real-time output from your scripts, including logs and errors.

Debugging Tips
- Use try/catch blocks to handle errors gracefully
- Log input values at the start of your script
- Check if keys exist before accessing optional data
- Test with the Test Action feature using mock data
- Start simple and add complexity gradually